■ Accucise Diagnostics Cardiovascular Disease Detection Solution
Fast: 5-min reaction time and 8-min first result reporting time with emergency TAT dramatically reduced
Accurate: Not interfered by biotin-streptavidin; Good clinical correlation
Stable: High precision with CV <5%; Accurate monitoring with assayed control
Flexible: Emergency mode available with on-demand testing; Fully automated cyclic sampling
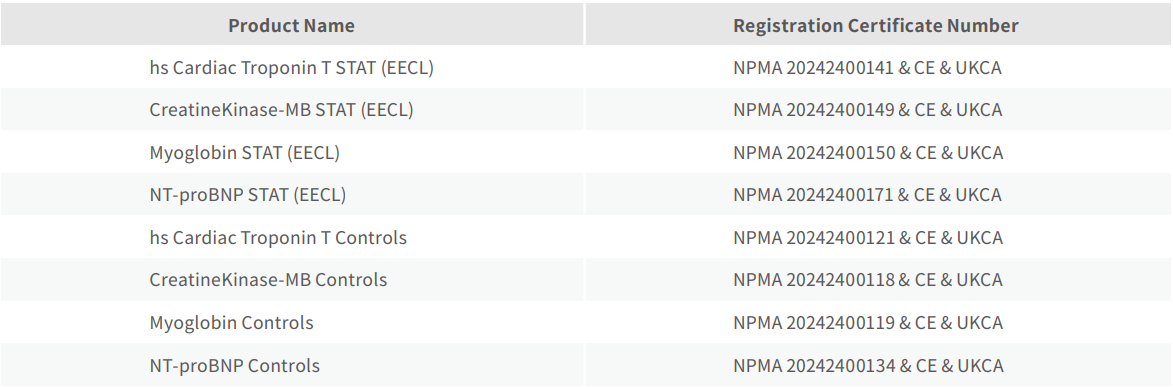
■ Product Registration Information
■ Cardiac troponin (cTn) is the “gold standard” for the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction and myocardial injury
Cardiac troponin (cTn) has revolutionized the approach to diagnosing, assessing prognosis, treating, and stratifying risk in ACS. Its use for diagnosing acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is a Class Ia recommendation according to international guidelines.
■ High-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) is a diagnostic marker of “early stage” of myocardial infarction
hs-cTn represents measurement of cardiac troponin with a high-sensitivity method. It aids in the detection of subtle myocardial injuries previously prone to being missed. This method enables earlier diagnosis or ruling out of AMI, provides a more appropriate approach to screening for high-risk individuals in the healthy population subject to cardiovascular events, and enhances clinical decision-making and prognosis evaluation.
In the 2020 ESC Guidelines for NSTEMI, a clinical triage of AMI within 0-1h through the use of hs-cTn results is explicitly recommended.
■ N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) is the most preferred marker for diagnosis and differential diagnosis of Heart Failure
B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) in the natriuretic peptide family and its inactive homologous fragment - N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) are of great value in the diagnosis of HF after myocardial infarction and the evaluation of the severity and prognosis. It is a Class Ia recommendation according to many clinical practice guidelines.
NT-proBNP can be used for risk stratification of patients with HF and ACS. Elevated NT-proBNP values in patients with HF suggest worsening of the disease and an increased incidence of complications and mortality. Similarly, ACS patients with elevated NT-proBNP values are at a higher risk of developing cardiac complications and have an increased mortality rate following myocardial infarction.